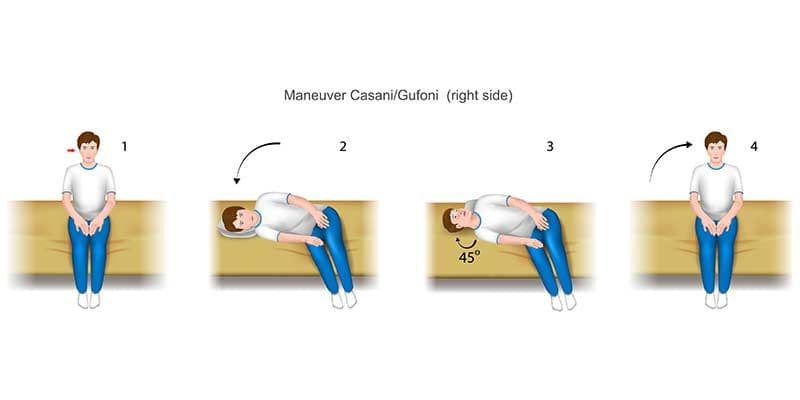
Horizontal Canal BPPV: Diagnosis and Treatment
What is Horizontal Canal BPPV?
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) is a common vestibular disorder that causes brief episodes of vertigo, typically triggered by changes in head position. While most cases of BPPV affect the posterior semicircular canal, about 5-20% of cases involve the horizontal (or lateral) canal, leading to Horizontal Canal Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (HC-BPPV).
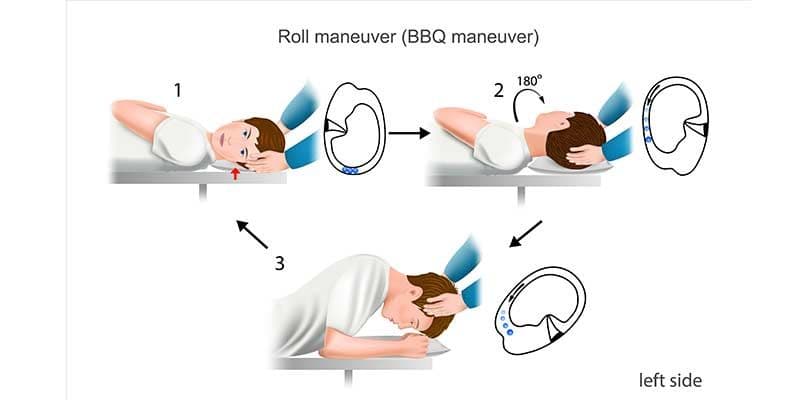
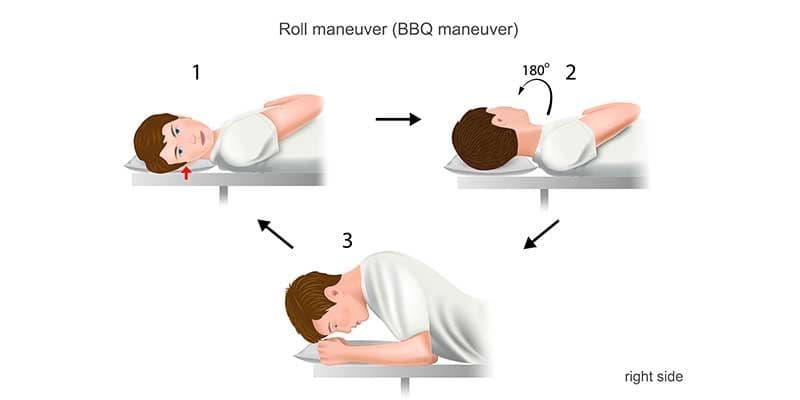
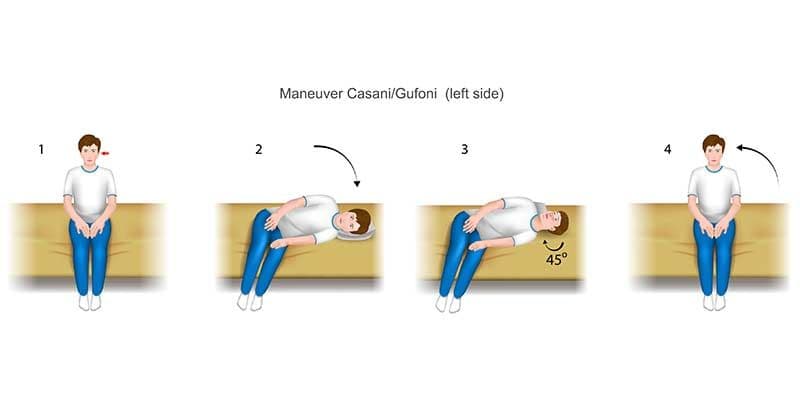
This condition occurs when otoconia, tiny calcium carbonate crystals, dislodge from the utricle and migrate into the horizontal canal, disrupting the normal flow of fluid and causing abnormal signals to the brain that result in dizziness or vertigo.
Diagnosing Horizontal Canal BPPV
Patients with HC-BPPV typically experience brief, intense episodes of vertigo triggered by specific head movements, such as turning the head to the side or rolling over in bed.
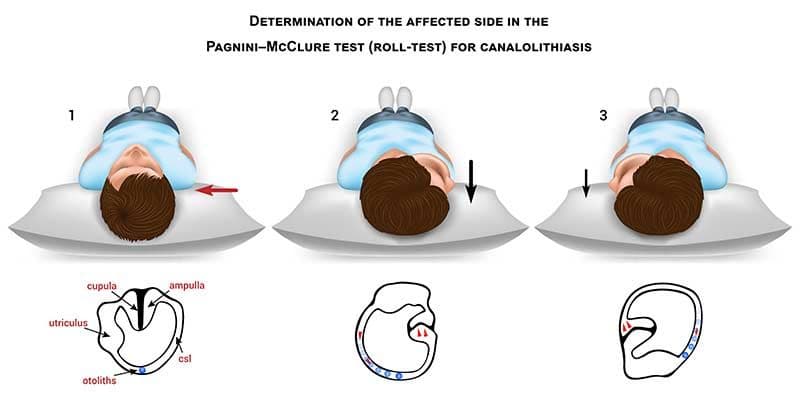
Unlike posterior canal BPPV, where vertigo occurs when looking up or down, HC-BPPV vertigo is often elicited by horizontal head movements. Nystagmus, a rapid involuntary eye movement, is a key diagnostic sign. In HC-BPPV, the nystagmus is horizontal and can be either geotropic (toward the ground) or apogeotropic (away from the ground), depending on the position of the affected ear.