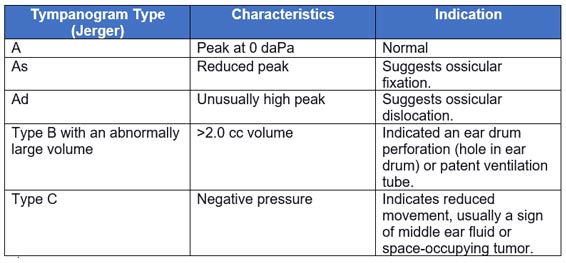
A tympanometry test is a non-invasive assessment of the compliance of the middle ear, i.e., its ability to transmit sound effectively. It measures the impedance of the middle ear by varying the air pressure within the ear canal and recording the corresponding changes in the eardrum’s movement.
The tester inserts a small probe into the ear canal during a typical tympanometry test. The probe consists of a speaker and a microphone (and an air pressure tube). The speaker emits a pure tone sound, which travels into the ear canal, while the microphone measures the sound reflected back. The air pressure tube is connected to a pump that systematically varies the air pressure in the ear canal, recording the amount of reflected sound as the air pressure changes.