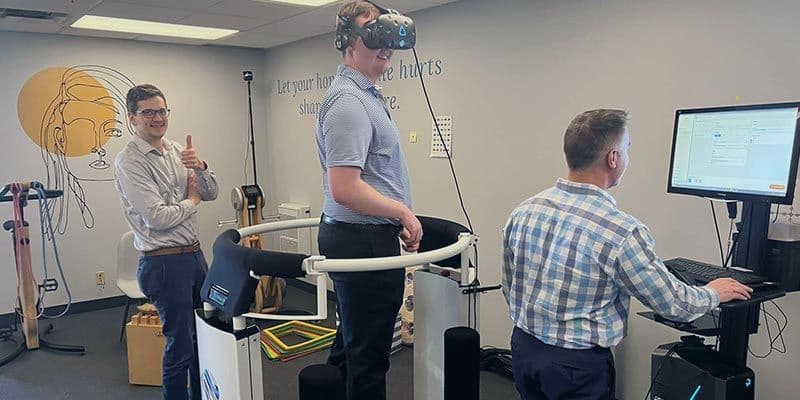
2. Artificial Intelligence: Shaping Personalized Treatment
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing physical therapy by enabling therapists to deliver care that is both highly personalized and proactive. AI-powered platforms analyze patient movement patterns, medical histories, and treatment progress, enabling the design of individualized rehabilitation plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
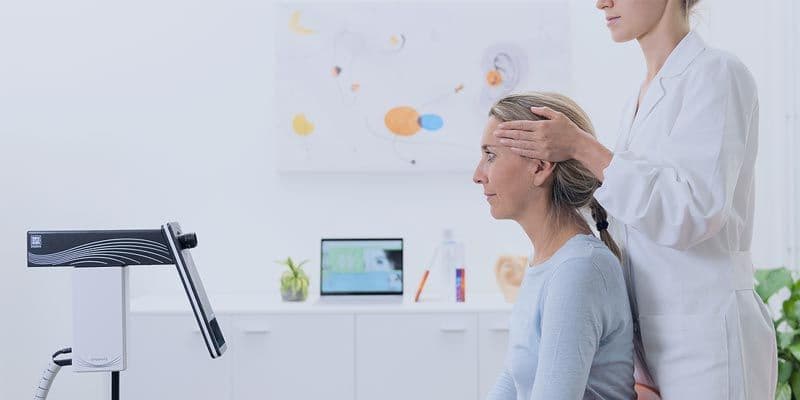
For example, AI-driven gait and balance platforms collect objective data during pre- and post-training assessments, allowing clinicians to track subtle changes in mobility and postural control. These systems can predict recovery times, highlight areas needing attention, and even suggest optimal exercise routines based on real-time feedback. The use of computerized dynamic posturography (CDP) systems further supports objective assessment of postural stability, helping therapists make informed decisions that improve patient safety and outcomes.
AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data also enhances pain management strategies. By continuously monitoring patients—using sensors and machine learning algorithms—therapists can detect early signs of discomfort or risk, adjust interventions promptly, and collaborate more effectively with other healthcare professionals. The result is a level of care that is not only responsive but also anticipatory, reducing complications and accelerating recovery.
3. Wearable Devices: Real-Time Monitoring and Data-Driven Care
Wearable technology is reshaping physical therapy by providing therapists with continuous, objective data about patient performance and recovery. Devices such as smart bands, sensor-equipped clothing, and wireless gait trackers measure metrics like posture, muscle activation, joint angles, exertion levels, and overall activity throughout daily life—not just during appointments.
This real-time monitoring supports more informed decision-making and enables therapists to adjust treatment protocols as patients progress. For instance, data from wearables can reveal subtle changes in gait or muscle strength, identify risk factors for falls, and document improvements in mobility. Physical therapists use these insights to refine exercise plans, set achievable goals, and motivate patients with visible evidence of their progress.
Wearable devices also empower patients to take an active role in their rehabilitation, providing feedback and reminders that encourage adherence to exercise routines. In sports injury recovery, therapists can track training loads and movement patterns, reducing the risk of reinjury and supporting safe return to activity. The increased availability of wearable technology in 2025 is making care more personalized, objective, and effective than ever before.
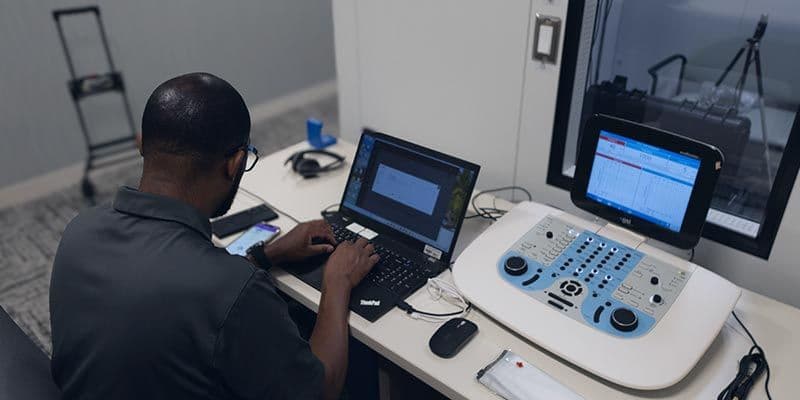
4. Biomechanics and Movement Analysis
Advancements in biomechanics and movement analysis tools enable physical therapists to deliver precision rehabilitation tailored to each patient’s specific needs. Motion capture systems, force plates, and high-resolution video-based analysis help clinicians understand joint movement, ground reaction forces, and muscle recruitment patterns during everyday activities.
For example, therapists use computerized dynamic posturography (CDP) and force plates to assess gait and balance objectively, identifying asymmetries or instability that may contribute to injury or slow recovery. By capturing data on how patients walk, stand, or perform exercises, clinicians can design interventions that target the exact deficits, whether related to muscle weakness, coordination, or postural control.
Biomechanical analysis is especially valuable for athletes, older adults, and patients with neurological conditions. It transforms evaluation and treatment into a more exact science, reducing guesswork, and improving functional outcomes. The integration of these tools with AI and wearable devices further enhances the ability to track changes over time and demonstrate measurable improvements.
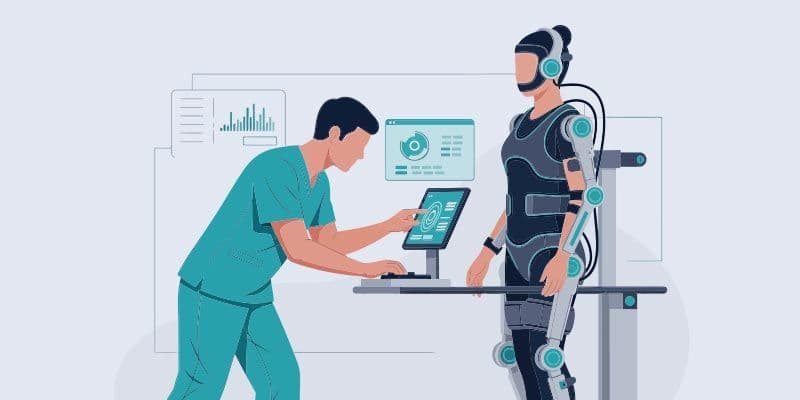
5. Robotics and Exoskeletons
Robotic-assisted devices and exoskeletons are emerging as essential tools in both neurological and orthopedic rehabilitation. These technologies provide precise, repetitive movements that are difficult to achieve manually, ensuring consistency and safety during therapy sessions.
Robotic gait trainers and upper limb exoskeletons help patients regain muscle strength, improve joint mobility, and relearn motor patterns following stroke, spinal cord injury, or major orthopedic surgery. Sensors built into these devices monitor patient performance in real time, allowing therapists to adjust parameters and optimize each session for maximum benefit.
By automating certain aspects of therapy, robotics frees clinicians to focus on higher-level assessment and individualized coaching. The result is a more efficient treatment that produces measurable, reproducible outcomes. As robotic technology becomes more accessible, its role in physical therapy will continue to expand, supporting patients of all ages and abilities.
6. Aquatic Therapy
Aquatic therapy remains a versatile and widely used modality, valued for its gentle strengthening and pain relief. The buoyancy and resistance of water enable patients to exercise with reduced stress on their joints, making aquatic therapy ideal for individuals recovering from sports injuries, managing chronic pain, or living with arthritis and mobility limitations.
Physical therapists integrate aquatic therapy with other modalities, using pools equipped with underwater treadmills, resistance jets, and specialized flotation devices. Patients can focus on improving balance, endurance, and flexibility in a safe environment that minimizes the risk of falls or injury aggravation.The supportive nature of water enables patients to build confidence, regain function, and transition more easily to land-based therapy as they progress.
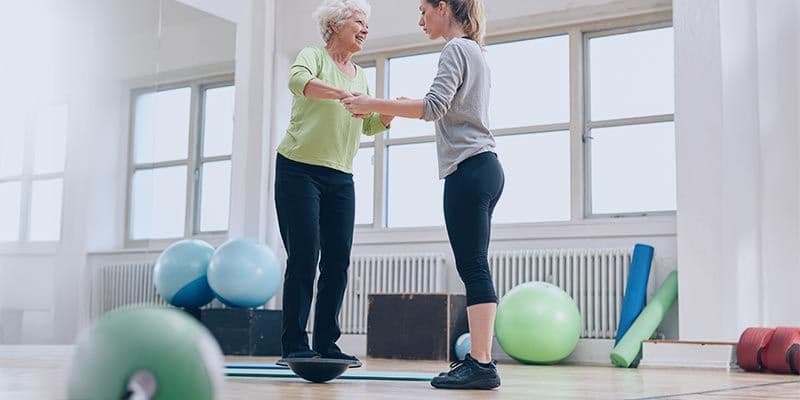
7. Preventive Physiotherapy
Preventive care is taking center stage in physical therapy, with clinicians increasingly offering programs that target mobility, gait health, ergonomics, and age-related changes before problems arise. Therapists conduct balance screenings and fall risk assessments using advanced balance assessment technology.
Early intervention through preventive physiotherapy helps patients maintain independence, avoid costly complications, and improve overall quality of life. Wellness programs may include education on safe movement, personalized exercise routines, and ergonomic advice for work and home settings. By positioning themselves as long-term partners in health, physical therapists are redefining their role from short-term rehabilitation providers to champions of lifelong wellness.
For older adults, regular preventive screenings can detect subtle declines in balance or strength, allowing for timely support and reducing the risk of falls. Athletes benefit from injury prevention strategies that optimize performance and minimize downtime. The proactive approach is driving a cultural shift toward healthier, more active communities.
8. Gamification
Gamification is rapidly gaining traction as an influential trend in physical therapy, revolutionizing how patients engage with their rehabilitation programs. By incorporating game-like elements—such as scoring systems, challenges, and rewards—therapists can boost motivation and adherence, turning routine exercises into interactive experiences.
This approach is efficient for pediatric patients and those recovering from lengthy injuries, as it helps sustain enthusiasm and encourages consistent participation. Through mobile apps, interactive platforms, and virtual competitions, gamification fosters a sense of achievement and community, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and a more enjoyable therapy journey.
9. Sustainability in Physical Therapy
As patients and providers become more aware of environmental impact, sustainability is emerging as a priority in physical therapy practice. Clinics are adopting digital forms and cloud-based reporting tools to minimize paper waste, using reusable materials, and investing in energy-efficient equipment to reduce their carbon footprint. These changes reflect a broader commitment to health that extends beyond individual patients, embracing the well-being of the community and the planet.
10. Telehealth and Remote Physiotherapy
Telehealth and remote care have quickly become integral to physical therapy, allowing patients to access expert care regardless of their location. Through secure video consultations, app-based exercise programs, and online progress tracking, therapists can deliver rehabilitation services to individuals in rural communities, those with mobility limitations, and busy professionals who struggle to attend in-person sessions.
This approach ensures continuity of care, enables therapists to monitor patient progress between visits, and fosters greater patient engagement in their recovery. Telehealth also supports group sessions, family education, and interdisciplinary collaboration, making physical therapy more adaptable, inclusive, and responsive to the demands of modern life. As digital health infrastructure continues to advance, telehealth is poised to expand further the reach and impact of physical therapy across diverse populations.
The Future of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is more intelligent, more connected, and more patient-centered than ever. Technology is at the heart of this transformation, with AI, wearable devices, virtual reality, robotics, and advanced biomechanics empowering therapists to deliver personalized, efficient, and engaging care. Preventive strategies, inclusive rehabilitation programs, and sustainability initiatives are expanding the reach and impact of physical therapy, supporting patients across the lifespan.
For healthcare professionals, understanding and embracing these trends is essential to delivering high-quality care in a rapidly changing landscape. Patients benefit from innovative treatment plans that promote recovery, independence, and lifelong wellness. As physical therapy continues to evolve, the focus remains clear: harnessing technology and compassion to achieve the best possible outcomes for every individual.